Top‑7 AI Motion Capture Tools 2025
A practical look at AI motion capture tools shaping animation, games, and education in 2025. Compare leading solutions, understand real use cases, and learn when custom AI motion capture systems make more sense than off-the-shelf tools.

ai motion capture
AI motion capture has quietly moved from experimental demos into real production workflows. Not because it looks impressive on paper, but because it solves everyday problems. A few years ago, capturing believable movement meant suits, markers, rented studios, and long setup times. Today, a camera, stable lighting, and the right software are often enough to get usable motion data.
This shift happened as models improved at reading human poses from regular video. Tools became easier to operate, faster to iterate with, and far more affordable than traditional systems. As a result, motion capture is no longer limited to large studios. Indie creators use it for animation tests, educators rely on it for training visuals, and game teams integrate it into early prototyping.
In this article, we look at seven AI-driven motion capture tools that matter in 2025. Along the way, we also touch on when off-the-shelf software is enough and when a custom approach makes more sense, including how Scrile AI can help teams build motion capture solutions tailored to their own products and workflows.
How AI Motion Capture Actually Works Behind the Scenes
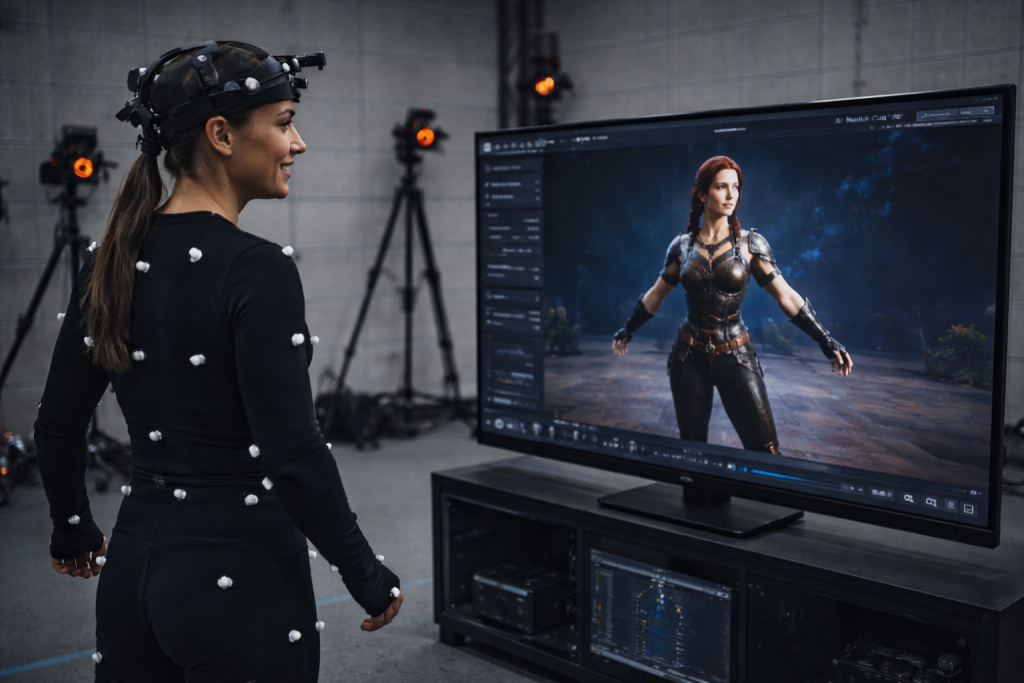

AI motion capture works by interpreting video as movement data. A camera records a person in motion, and the software studies how posture, balance, and joint positions change from one moment to the next. Instead of measuring the body directly, the system analyzes visual cues and reconstructs motion as a digital skeleton that can be applied to animation or 3D characters.
Older motion capture pipelines depend on markers, suits, or depth sensors. They deliver accurate results, but they also demand controlled spaces and long preparation. Motion capture AI takes a different route. It relies on machine learning models trained on large collections of real human movement. Those models recognize common motion patterns and use them to interpret new footage, even when conditions are less than ideal.
That learned behavior is what makes AI motion tracking usable in everyday settings. The software understands how bodies usually move, so it can handle partial visibility, uneven lighting, or casual environments. A raised arm, a step forward, or a turn of the torso is recognized based on probability and context, not hardware signals.
Single-camera setups are common because they’re quick to deploy and easy to scale. Multi-camera setups add consistency when movements become faster or more complex. In both cases, AI tracking converts ordinary video into motion data that teams can refine, export, and reuse across animation, games, and educational projects.
Where AI Motion Capture Is Used Today
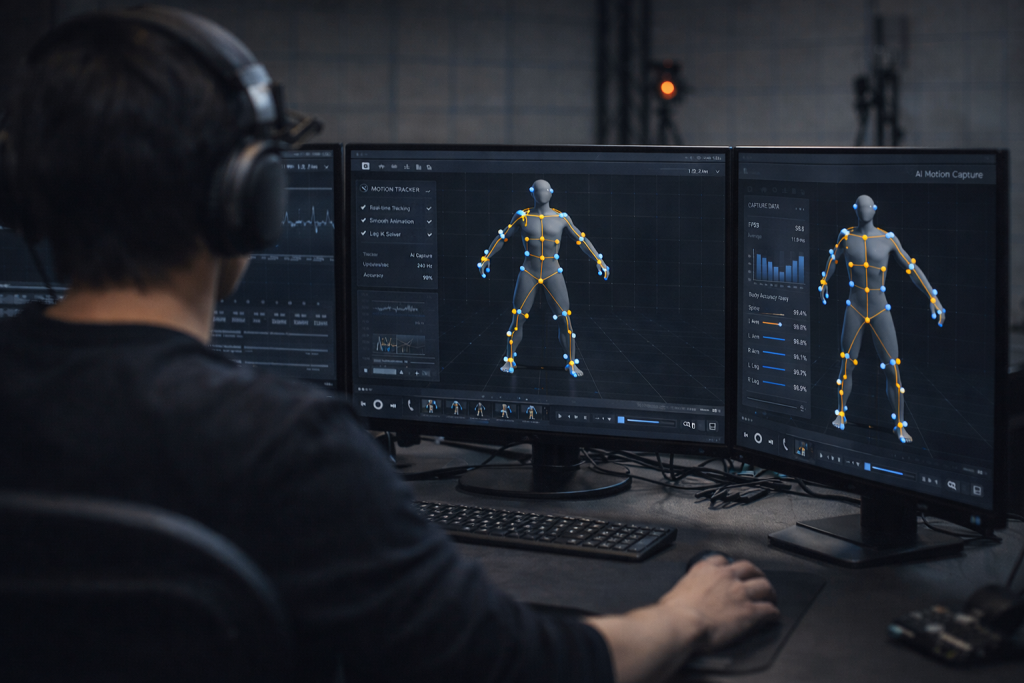

AI motion capture spread fastest in fields where speed matters more than perfect data. Teams already working with tight deadlines and small crews saw immediate value and started using it as a practical tool rather than a replacement for high-end mocap.
In film and animation, it’s often used early. Directors and animators rely on it to sketch scenes, test pacing, and explore character movement before committing to final animation. For smaller studios and freelancers, it also becomes the final source of motion, not just a draft.
Game developers use it heavily during prototyping. When mechanics are still changing, waiting for a full capture session slows everything down. AI capture lets teams try ideas quickly and throw them away just as fast.
Education, sports, and training environments adopted AI mocap for accessibility. Classrooms, gyms, and remote setups don’t allow complex equipment, but they still need visual movement examples.
Across these industries, usage usually looks like this:
- Previsualization and early animation, where rough but believable motion helps teams make creative decisions before investing more time
- Gameplay and interaction testing, where movement supports mechanics, camera logic, and player feedback rather than final visuals
- Training and instruction, where showing correct form, posture, or motion sequence is more effective than static explanations
These sectors moved first because AI motion capture fits their everyday constraints and keeps production moving without heavy setup.
Top 7 AI Motion Capture Tools to Watch in 2025
Before diving into specific tools, it helps to explain how this list was formed. The focus isn’t on flashy demos or marketing pages. Selection here is based on how well each tool handles markerless tracking in everyday conditions, how easily motion data can be exported into real engines and editors, and whether the workflow actually holds up once a project gets moving. Stability, learning curve, and repeatability matter more than novelty.
RADiCAL
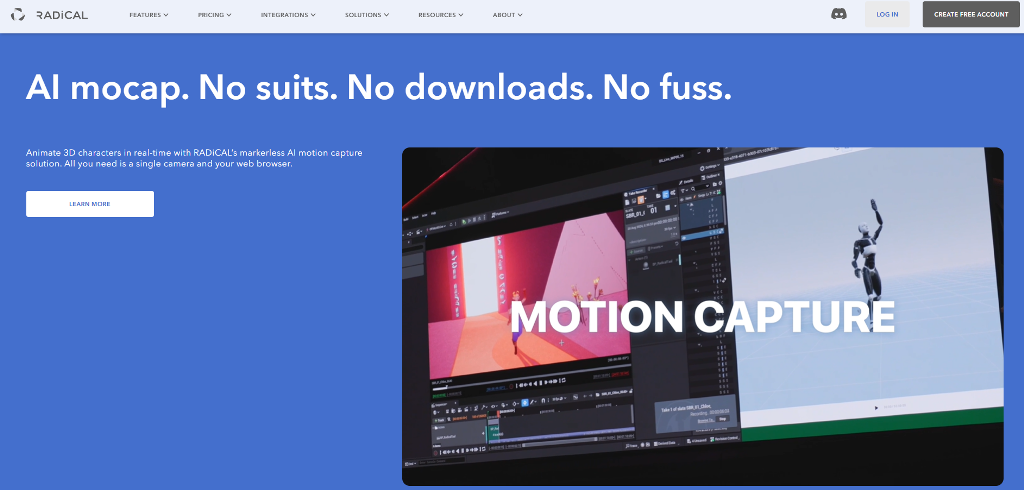
RADiCAL is one of the clearest examples of AI motion capture working at scale. It turns regular video into motion data directly in the browser, which lowers the entry barrier dramatically. Creators can upload footage, process it online, and export results without building a complex local setup. Desktop workflows are available for teams that want more control, but the browser-first approach is what made RADiCAL popular with indie animators, educators, and small studios. It’s often used for previs, animation blocking, and early-stage character work.
DeepMotion
DeepMotion focuses heavily on character animation and game-ready output. Its strength lies in producing motion that feels clean enough to drop into rigs with minimal adjustment. The system works well with common 3D pipelines and game engines, which explains its popularity among developers. When people refer to deep motion AI, they usually mean this balance between accessibility and animation-friendly results rather than raw capture precision.
Rokoko Vision
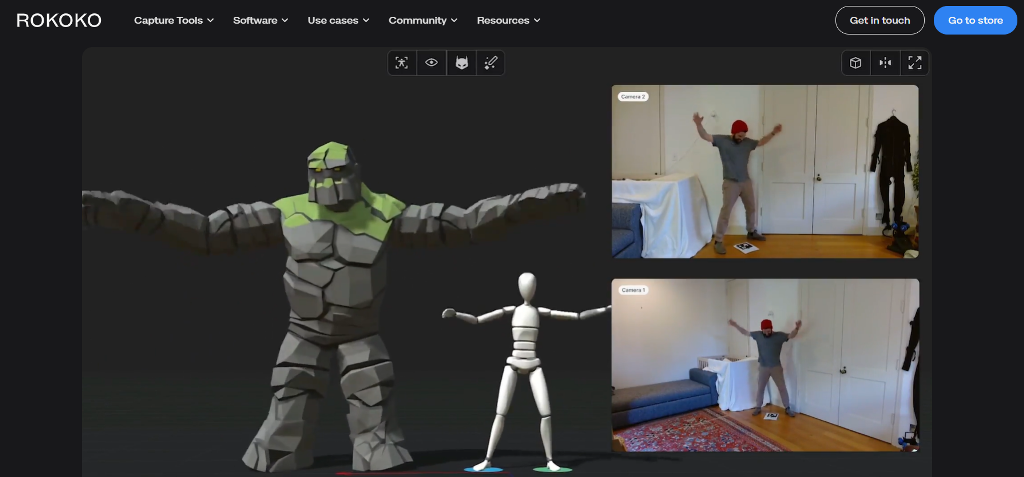
Rokoko Vision targets creators who already work with webcams or mobile cameras. It fits naturally into lightweight setups and doesn’t demand studio conditions. Indie creators often use it to add motion to short animations, social content, or experimental projects. While it won’t replace multi-camera systems, it works well when speed and simplicity matter more than perfect tracking.
Move AI
Move AI sits at the other end of the spectrum. It relies on multi-camera setups to achieve higher fidelity and consistency. The payoff is more reliable capture during complex movements, but the setup requires planning, space, and calibration. Studios choose it when they need precision without returning to traditional marker-based systems.
Plask
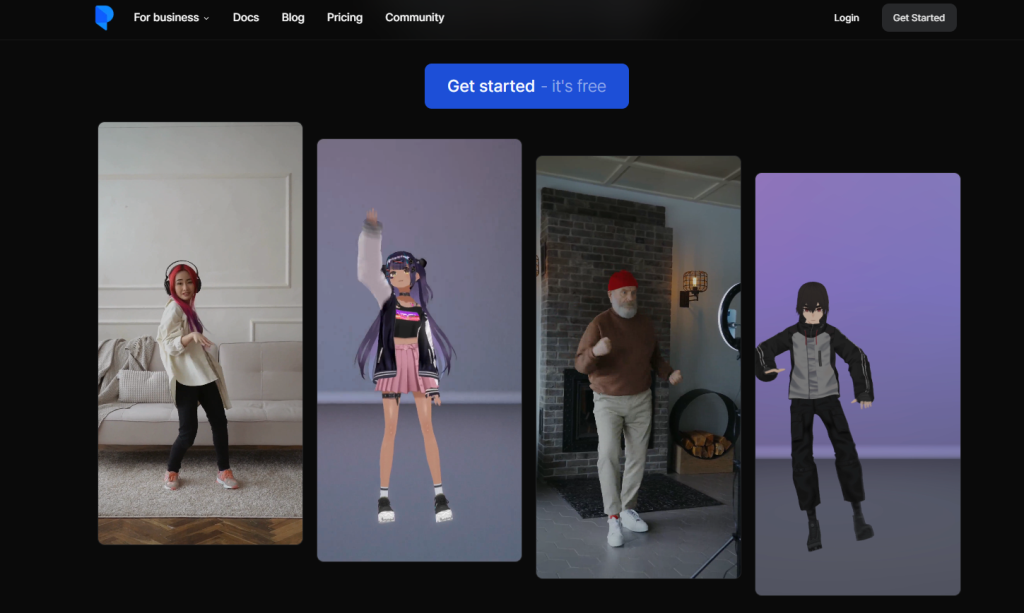
Plask is often picked for its gentle learning curve. The interface feels approachable, and the workflow is built around fast turnaround rather than perfect data. Animators use it to rough out movement, test ideas, or generate placeholder animation that can be refined later. For quick prototyping, AI motion capture here acts more like a sketching tool than a final recorder, which is exactly why it works well in early production stages.
Sency AI
Sency AI comes from a different angle. Its roots are in fitness and sports, and that focus shows in how it treats movement. Instead of aiming purely at animation, it emphasizes form, repetition, and feedback. Coaches and trainers use it to analyze posture and motion in near real time. While it’s less flexible for cinematic animation, it shines in environments where understanding how a body moves matters more than visual polish.
Custom AI Mocap Pipelines
Some teams eventually move past ready-made tools altogether. This usually happens when workflows become specific or scale introduces friction. A studio may need tighter integration with its engine, custom export formats, or motion data tailored to a unique character system. In these cases, building a custom pipeline around AI motion capture makes more sense than adapting off-the-shelf software. These setups often combine trained models, internal tools, and domain-specific logic to match how the product actually works.
Building Custom AI Motion Capture Systems with Scrile AI

As teams spend more time with off-the-shelf AI mocap tools, a pattern usually appears. At first, the software feels fast and flexible. Over time, limitations start to surface. Export formats don’t quite match the pipeline. Motion data needs heavy cleanup. Integration with a game engine, learning platform, or internal tool becomes awkward. This is the point where a custom approach starts to make sense. This is the point where Scrile AI steps in.
Scrile AI is not a motion capture tool you download and run. It’s a custom development service focused on building AI-driven systems around real product requirements. Instead of adapting your workflow to a generic solution, Scrile helps design motion capture pipelines that fit your AI characters and avatars, your data, and your platform logic. That includes choosing the right models, defining how motion data is processed, and embedding it directly into existing products.
This approach is especially useful when motion capture plays a core role rather than a supporting one. Educational platforms may need motion analysis tied to feedback and scoring. Games may require motion data aligned with proprietary rigs and physics systems. Interactive products often need personalization that standard tools simply don’t offer.
Ownership is another factor. With a custom system, teams keep control over their data, their models, and how motion is reused or retrained over time. That flexibility matters as products evolve.
What Scrile AI Can Build Around Motion Capture:
- Custom machine learning models trained on domain-specific movement patterns
- Direct integration into games, apps, or learning platforms without manual workarounds
- Scalable pipelines that support personalization, updates, and long-term growth
For teams moving beyond experimentation, custom AI motion capture becomes a way to align technology with the product, rather than shaping the product around the technology.
Conclusion
AI motion capture has settled into everyday production because it solves real problems. Teams use it to move faster, test ideas earlier, and reduce dependency on complex setups. Ready-made tools work well when speed and accessibility matter most. Custom systems make sense when motion data needs to fit tightly into a product, a pipeline, or a business model.
That choice comes down to how central motion capture is to your work. As AI mocap becomes part of mainstream pipelines, more teams start looking beyond templates and fixed features. When that happens, having a partner who can design around your needs matters. If you’re building something that goes past off-the-shelf tools, it’s worth reaching out to the Scrile AI team and discussing a custom approach.
FAQ
What is motion capture AI?
Motion capture AI uses machine learning models to interpret human movement from video. Instead of tracking physical markers, it relies on pose estimation and learned motion patterns to convert visual input into usable motion data for animation, games, or training.
What is AI motion detection?
AI motion detection focuses on identifying movement within a scene rather than recording detailed body motion. It’s commonly used in security systems, access control, and monitoring, where detecting entry, direction, or repeated movement matters more than full motion capture.
What is the use of AI in motion graphics?
AI helps automate repetitive animation tasks such as rigging, pose generation, and cleanup. It speeds up 3D workflows by handling technical steps in the background, allowing artists to focus more on creative decisions and iteration.
